|
0 Comments
 “Without imperfection, neither you nor I would exist.” ~ Stephen Hawking The politicians, pundits and journalists who are against the Iran Nuclear Agreement focus on one point: it’s not perfect and could be better. Most of us know from experience that humans are not perfect. Isn’t it unrealistic to expect that any agreement created by imperfect beings be perfect? We are not in a position to force capitulation. Negotiation is a process that creates a path forward in which each party retains its dignity, propelled by the desire to give up something of personal value in order to gain something of greater value for everyone. Agreements are never perfect. If Congress thwarts this agreement, what are the alternatives? We could continue and even increase sanctions, but our allies will not stand by our side, and if we are the only country applying sanctions the effects will be minimal—not a perfect alternative. Fifty years of embargoing and sanctioning Cuba has shown us that these alternatives can and will cause increased defiance. We imposed strict sanctions on Russia, yet Putin doesn’t seem a bit inclined to return Crimea. We could also go to war, but we all know how imperfect war is. We only have to look at recent history to remember that in modern war there is seldom a clear winner and the costs are staggering and tragic. Consider: Korean War: No winner emerged. Instead, Korea remains divided and the North retains the capability of making a nuclear bomb(s). The war was waged at a great cost in terms of money and lives. Vietnam War: Objectively, North Vietnam, the communists, achieved their goals of reuniting and gaining independence for the whole of Vietnam, and it remains under communist rule today. The U.S. dropped more than 7 million tons of bombs—more than twice the amount that was dropped on Europe and Asia in World War II—and we lost more than 58,000 young lives. Not a perfect solution or result. Gulf War: The aftermath of the Persian Gulf War appeared to be a victory, but what we learned is that the victory was hollow. Saddam Hussein was not forced from power and the region became less stable. Many believe that this war helped to make Al Qaeda a force that would later strike our homeland. Iraq War: The initial stage of the war was a raging success—the banner proclaimed “Mission Accomplished.” Yet, the war created eight years of sectarian violence, 4,900 American lives lost and many more severely injured, and it amounted to a trillion dollar debt from which we still haven’t recovered. Iraq is still incapable of defending itself, and it gave rise to ISIS. We need to ask ourselves if an imperfect agreement that may produce peace and diminish the potential of a nuclear Middle East is a better risk than the alternatives. Or are we willing to put our country and the world at risk by pursuing alternatives that have a dismal and tragic record. Can we afford to risk isolating ourselves from our allies, countries critical to solving the world’s most urgent problems? Are we willing to once again shed the blood of our youth by waging war? Writer Archibald McLeish said, “There is only one thing more painful than learning from experience and that is not learning from experience.” We have a clear choice. The Iran Nuclear Agreement has risks, but experience has shown that the alternatives are much more costly in terms of world standing, capital and human lives. All our options are imperfect and risky, but the greater risk here is repeating the past when we have a chance to take a risk for peace instead. 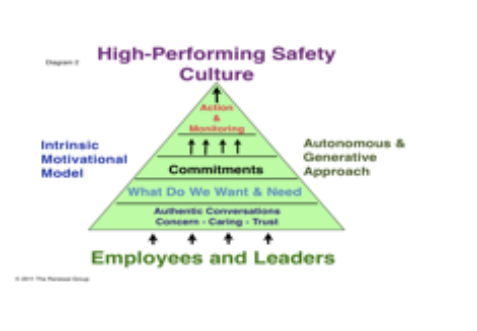 Normally, you assess an organization’s safety culture by observing how employees translate the company’s principles, values, attitudes, and goals into their behavior and decision-making. This seems like a pretty straightforward method, but beware of drawing conclusions based only on observations—you’ll fall into the assumptions trap. I’ve fallen into this myself by relying on direct observations and reports consisting of data based on observations, and I suspect I am not alone. The assumptions trap is a consequence of the way in which the human brain forms patterns to help us manage a complicated life more efficiently. Patterns feed our assumptions. They help us react, predict and make decisions regarding situations without having to assemble and sift through all of the details of what we are observing. The problem is the brain has no investment in making distinctions between fact and fiction. It takes in what it sees, dismisses what doesn’t fit, and draws a conclusion as expeditiously as possible. It will even add in data to fill any gaps just to complete the picture to fit the established pattern. This works very well when we need to slam on the brakes to avoid a child who darts into the road. However, this process has limits when used exclusively to assess or make assumptions about the effectiveness of a safety culture. David McLean, Chief Operating Officer for Maersk, expressed this realization in his article “The Importance Of Process Safety & Promoting A Culture of PSM.” “We were all very good at measuring personal safety performance, i.e. slips, trips, and falls, and this is very tangible, but did a good personal safety record mean we had a safe operation? Clearly not, as several major accidents had proven.” Avoid the Assumptions Trap by Engaging in Conversations “Can you hear me now?” was the key refrain from a Verizon commercial a few years ago. If you listen, you can hear employees using this same refrain in regard to their relationship with their managers. “They never listen to us, and when they do, they don’t hear what we are saying,” I’ve heard employees say. “They already have their minds made up.” Consider for a moment that managers spend 75% to 90% of their time in conversations! Who are they having these conversations with? And are they really listening or just filling in the gaps of existing beliefs and patterns? To understand and know one’s culture you must listen to it—not just to the words but also to the emotional texture of the words. A safety culture is created, nurtured and sustained by the breath and quality of the conversations that take place and the ones that don’t. “What people say and what they withhold matters,” said David Arella, founder and CEO of 4Spires. “Language trumps control. How the communication is initiated and conducted is often more important than what is communicated. An organization is a network of person-to-person work conversations during which information and energy is exchanged. Like cells in your body, the quality of these work-atoms determines the effectiveness of the whole. Attending to and influencing work conversations can help transform culture and improve collaboration.” The true nature of a culture is revealed through its conversations. If you want to understand your culture before making assumptions about your culture’s strengths and weaknesses—what motivates employees and what’s in their hearts and minds—you must engage in open and honest talk. Conversations can help give meaning to observations. Culture is made up of layers of conversations that are constantly vibrating and emitting information. Learning to notice and listen to these waves of information is a critical culture competency. It requires that leaders be committed to moving through the casual and superficial noise in order to gain insight into the organization’s authentic culture and discern what is really motivating employee performance. Don’t Use Data: How to assess your safety culture more effectively Edgar H. Schein, PhD, considered to be one of the foremost experts on organizational culture, believes that if you want to access your organization’s culture, bring together a group of employees who represent each part of the organization and provide an opportunity for them to dialogue about their issues, concerns, and the strengths and weaknesses they experience and perceive in the safety culture. Here is a simple but effective model to help organizations assess and transform their safety culture. It calls for leaders, managers, supervisors, and employees to engage in authentic conversations in which each can express and share their concerns and build the trust required to move forward. Leaders frequently expressed that they had reservations about engaging in these conversations, particularly those that reached below the surface. They preferred to use a survey (hard data). But after working with this model, not only did they obtain the data they wanted; they gained the commitment they needed from employees to work toward common goals. The following questions can help assess if your have a culture that values conversations or if it is reliant on assumptions and patterns. · Is it like pulling teeth to get employees to talk in meetings? · How often do safety leaders practice walking and talking about the site? · Is the word stupid—or a similar insult—ever used to describe safety incidents or the employee involved? · What emotion(s) best describes the mood of the safety culture? Frustration, boredom, disappointment—or excitement, curiosity, and passion? · Do managers abhor meetings and feel that they are a waste of time? · How often have employee safety recommendations been implemented? This self-assessment will begin to give you an indication if the conditions of your safety culture are conducive to meaningful dialogue; if it encourages open and honest conversations or stifles it. A word of caution though: Just because employees may be reluctant to engage in conversations doesn’t mean they don’t want to be heard. Their behavior may be more about their lack of trust, fear of blame, or a result of previous conversations that resulted in a negative experience. A positive safety culture is a repeatedly observant one, not just of behavior but also of its tone and content. Safety leaders would be well served to develop a practice of deeply listening and observing before making assessments and judgments. Contact Tom Wojick for more information on how to introduce conversations into your culture 401-525-0309 [email protected]  I can’t seem to get through a page of John Gardner’s book Self-Renewal: The Individual and the Innovative Society—which is full of lessons, advice and wisdom on the nature and nurturing of self-renewal—without being struck by a concept that resonates deeply. The following is just one example: “For every citizen movement that changes the course of history, there are many thousands that hardly create a ripple. The few movements that survive are those that speak to the authentic concerns of substantial numbers of people.” Immediately, names like Mahatma Gandhi, Martin Luther King, Jr., Susan B. Anthony, and Harvey Milk come to mind. These individuals were able to profoundly articulate the authentic human and civil rights concerns of millions of disaffected people, and because of this they became leaders within movements that changed societies. The ability to sense, understand and authentically communicate the concerns of others is the core of leadership, and it’s as important in leading organizations as it is in large-scale societal change, because at the heart of all workplaces are people with concerns. An alternative perspective on engagement Organizations that achieve high levels of employee engagement experience superior results in many critical performance and success metrics, including revenue. And yet for many leaders, engendering deep levels of stakeholder engagement appears to be a difficult challenge. Too often I’ve heard leadership teams, when considering an engagement effort, say, “You can never satisfy them; if we change, they’ll only find something else to complain about.” This perspective of engagement, about giving in or giving up something, is a formula for failure. An alternative perspective that I recommend to leaders is to frame engagement as a “concern movement”: a process of recognizing and attending to the mutual concerns of both management and employees. The foundation of a concern movement In his book Moral Courage, Rushworth Kidder identifies the values of honesty, responsibility, respect, fairness, and compassion as core human values. The foundation of a concern movement starts with a focus on these five universally accepted values, which, when invoked and practiced by leaders, speak to the essence of human concerns. Honesty, responsibility, respect, fairness, and compassion transcend all cultural and organizational demographics. When they flourish, so does human engagement. To build a culture of engagement, organizations must integrate these values into the “why” and “how” they lead and the structures and systems of their operation. This approach doesn’t require a leader to be a great orator, or to risks one’s safety for a movement—but it does require that you recognize and understand your stakeholders’ concerns and to be able to authentically resonate with their concerns. Values are the powerful “why” that influence what people do and how they do it. Try delivering bad news to your organization without respect and compassion; it will inflame passions, kill engagement, or both. When employees perceive their organization to have a disregard for basic human values, it takes a toll on organizational results. On the other hand, the benefits of employee engagement are well documented, and the road to engagement is paved with core human values. Organizations willing to walk the walk and talk the talk and start their own concern movement will succeed—both personally and as a whole.  Which side of the divide are you on - are you a We or They? The they’s and we’s have been at odds before the Hatfields and McCoys starting shooting at each other. The We–They Divide is not unique or new. It has existed since the dawn of employee-manager relationships and to this day it continues to infect, constrain, and confound organizations and leaders. The impact of the We–They Divide on an organization is similar to any infection: Inevitably, it takes a toll on everyone. It diminishes work efficiency, quality, and organizational resilience, and can be the difference between success and failure.
The divide is not just an employee satisfaction or morale issue, though; it strikes at an organization’s bottom line. Towers Perrin’s 2008 Global Workforce study found that We–They Divides have negative consequences on operating margins, but, conversely, if a divide is reduced it can improve an organization’s bottom line. With all the financial, quality, performance, safety, and competitive risks this kind of divide exposes an organization to, and with all the research that validates its existence, why do organizational leaders continue to underestimate its impact? For many, the We–They Divide is untraveled territory with few or trusted maps available to assist them in navigating their way. Traditional organizational constraints like limited financial resources are issues most leaders feel equipped to handle. They can close gaps by reducing or cutting expenses, look for additional financing, or increase revenue by reaching more customers or raising prices. When it comes to the We–They Divide, the solutions are less formulaic. Feeling less confident, lacking in experience, and without training in how to recognize and approach the issue, many leaders are slow to address divides in their workplace. One manager explained to me, “We have only one chance to get this right, therefore we need to go slow.” While slow approaches usually indicate thoughtfulness and precision, in this case it indicates a lack of experience, confidence, and trust. The manager’s adherence to a slow approach only increases the chances that his workplace’s infection of disconnection will spread and widen the divide, making treatment that much more difficult. Employees are more concerned about serious commitments to address the We – They Divide than they are of mistakes. What Is the We–They Divide and the Reality of Perception The Conference Board, a global, independent business membership and research organization working in the public interest since 1916, developed a definition for a concept called employee engagement, which describes the degree of emotional and intellectual connection or disconnection an employee has for his/her job, organization, manager, and coworkers that, in turn, influences and motivates him/her to give and apply additional discretionary effort to his/her work. The We–They Divide is the emotional and intellectual distance between leaders and employees—it is the degree of disconnect. Human behavior is based on perception. Therefore, whether correct or incorrect, fair or unfair, perceptions are each person’s (group’s) reality, and it is these perceptions that create the divide: We Perceptions vs. They Perceptions. Our perceptions create a set of default assumptions that remain the undercurrent of our thoughts and feelings regarding any given topic. A common perception I hear from employees concerns the “invisibility of leaders.” It sounds like this: “We never see him. The only time he leaves his office is when something negative happens. Then he’s in our face wanting answers.” It’s not difficult to predict the assumptions that could arise from this type of perception. While some employees might assume their leader doesn’t care about them, others might assume you only receive attention when you do something wrong. The worst? Some might believe their leader thinks he or she is too good to associate with them. Sadly, most leaders are taken aback to hear of their employees’ assumptions. “I never knew.” While some immediately commit to change, others start explaining, defending, and offering examples of employee engagement. The space between these two perceptions is another example of the We–They Divide. Though some believe they cannot control what others think and assume, and that “no matter what is done employees will always find something else to complain about,” we know this not to be the case. There are a number of methods and approaches that leaders and organizations can take to reduce divide. There are six We -They Divide Prevention Measures leaders can take to positively influence employee perceptions and assumptions that will prevent the divide from widening—and even begin to reduce it. However, it does takes a much more comprehensive initiative to transform a We–They Culture in which employee disengagement is a serious impediment and threat to an organization’s optimal performance to a We Culture. For insight how a client organization accomplished this read, Leaders Don't Motivate - They Create The Conditions For Self-Motivation on this site. The following are We–They Divide Prevention Measures taught by Nicole Gravina, Ph.D. When leaders integrate and apply these concepts while making decisions, communicating with employees, designing systems/processes, and working with each other, they can minimize the perception of the divide and increase cooperation and commitment from employees. Proximity: Employees take particular notice if leaders are in close proximity or if they are distant, and the perception of distance increases the divide. Therefore, a lack of physical, social, and emotional presence by a leader contributes to negative perceptions and assumptions in the We–They Divide. Communicating primarily by email, not attending or holding employee meetings and the absence of informal social contact in meetings, and being absent at informal and formal social events can all contribute to the perception that a leader doesn’t like us, care about us, or understand us. Leaders must be proactive in their efforts to finding ways to bring themselves into closer proximity with their employees. If your office is distant from the people you manage, schedule time on a regular basis to leave your office and meaningfully interact with your employees in their space. Take time to learn about their social and family situations. Engage on a social level. Similarity: is to work against the common perception that leaders are better and more privileged than their hourly workforce. Employees understand that leaders are paid differently and have additional benefits, but they don’t like when their leaders present themselves as better, smarter, wiser, or more privileged. The more you can emphasize your common human similarities, the closer a connection (emotional proximity) will be between a leader and his/her employees. Though you may be fortunate enough to rise on the corporate ladder, never lose sight of where you came from and the people who helped you climb that ladder along the way. Much to their disadvantage, leaders operate in bubbles and cast long shadows. Seldom do they receive unvarnished feedback, which they need in order to understand employee perceptions and behavior. To be an effective leader, one must create opportunities and structural mechanisms that allow for unfiltered feedback. Inconsistent Application of Rules and Policies: Nothing is more irritating to employees—or sends the “I’m better” message—than when leaders excuse themselves from basic workplace policies. Management should always demonstrate its similarity and commitment by adhering to its own rules. Opposing Goals: Are the goals established in various areas of the organization interdependent or independent of the organization’s overarching mission? I have seen incentive structures for a sales groups conflict with the corporate responsibility and quality departments, and instances when safety procedures and goals in a manufacturing organization are not followed because they would have interrupted production goals. Is your team aligned? Differences in Availability of Resources, Time, Feedback, and Recognition: Everyone notices if someone else gets more than they do. If you had brothers or sisters, you know what I mean. Leaders need to be attentive to this aspect of human nature. If an employee or a group of employees perceives that someone is getting more than they are, not only will they think this it unfair, they’ll also feel less important. I’m not simply referring to hard resources like money and equipment, but the softer and less tangible resources such as demonstrations of appreciation and recognition. Though many leaders don’t value recognition as a resource, employees do. Leaders who understand and develop a practice of appreciation and recognition are providing employees with emotional and psychological resources that will motivate and strengthen their commitment for years to come. Lack of Information and Follow-Through: Assuming people know and understand your intentions and your purpose, and that of the organization, is a mistake. Communicate, communicate, and communicate more. Leaders must set a goal to actively communicate and solicit feedback from employees and not stop until you hear, “You’re killing us with all this communication!” Once you hear this statement, you’ll know you’re on the right track. Follow-through is the period at the end of a sentence. One of the downfalls of employee suggestion programs is that employees seldom get feedback or follow-through on the status of their suggestion. Employees will hang onto an issue until they feel the loop has been closed, leaders must follow through, which in turn builds trust. A colleague of mine, Richard Hews, instructs managers on the “Cycle of Commitment or Promise. One of the essential aspects or steps in the cycle is the declared satisfaction. It is here where the initiator and the performer declare their satisfaction if the request was completed to the requirements. Punishment-Oriented Culture: Nothing is more destructive than a culture in which a hammer is the primary leadership tool and every employee feels like a nail. It is divisive, creates aggression, and kills engagement. No high-performance culture is built on a foundation of punishment. This type of culture only exacerbates the We–They Divide, turning it into a chasm. Summary The We–They Divide is a silent and serious threat that can strike the bottom line of an organization and jeopardize its stability and competitiveness. Disaffected and disengaged employees lack the commitment, creativity, and energy to give their discretionary effort. And in a continuously changing and challenging global marketplace that rewards efficiency, quality, service, and dependability, a disengaged workforce diminishes the ability and capacity to deliver on these requirements. As serious as the consequences of the We–They Divide are, the benefits of crossing and closing the divide are that much greater. An engaged workforce not only contributes directly to an organization’s bottom line, but it also provides energy, commitment, and resilience in a world in which the potential for adversity is just around the corner. Ultimately, the We–They Divide is about relationships. It’s not about giving and taking and winning and losing; it’s about respecting and responding to basic human needs. Take the first step and discover how rewarding leading a WE culture can be personally, professionally, and organizationally.  I was spellbound. Here I was not reading a book about teams, but listening to the wisdom of a team who had lived it day in and day out. This experience occurred during a recent workshop on workplace safety. I had the privilege of working with a high-performing team that has a stellar safety record. The purpose of the workshop was to invite additional dialogue regarding a survey the team had taken. The plan was to seek additional detail and nuance about what they were thinking, feeling, and the experiences that influenced their ratings in this survey that measured areas of safety in their workplace ranging from corporate ethics to hazard recognition. While others took some time to warm to the task, this group was immediately engaged. They didn’t need encouragement or assurances of confidentiality. They jumped right in to a lively dialogue on each section. It wasn’t long before my curiosity was killing me—how was this group so invested, open, engaged, honest, and committed not just to safety, but to everything else they did? So I gently interrupted our conversation. “Can I deviate for a moment from the agenda and ask what drives your team and keeps all of you invested and committed to what you’re doing and how you do it?” Immediately, they started to share the glue that binds them together in their common pursuit of safety and performance. The first thing out of their mouths was a statement that indicated they each held a sense of common mission and purpose that drove their thinking, feelings and behavior. “We are very aware that what we do is very dangerous. One mistake has the potential to not only injure one of us—it could also have serious consequences for the people at this plant and the surrounding community. We don’t ever want that to happen.” What came next was, “We know each other and we care about each other.” And the caring extends to wives, children, girlfriends, and boyfriends. “We know a lot about each others’ families; we know their names, what schools they go to, the sports they play, and when things are going good and not so good. When you know people’s families, you have a deeper understanding that what we’re doing and how we’re doing it has far-reaching consequences. This also helps us to keep in touch with how a person is doing personally, and sometimes we pitch in to give a coworker a break when he or she needs it.” More Glue: We agree to disagree. “It’s taken us some time, but we’ve come to the conclusion that disagreeing is just part of life. We don’t get that upset anymore when we disagree. We give each other space and sooner rather than later we come around and work things out. We know that nothing is more important than safety and that keeps us from going off on each other.” We take personal accountability for our actions. “This has also taken us some time, but we’ve come to accept that we are the ones who can make a difference. It doesn't do us any good to complain, blame and look to somebody else to make our decisions. Our behavior and choices make the biggest difference, and we feel more secure and satisfied being accountable and in control.” This team had no formal training in teamwork; they had only learned from their experiences and continued to put what worked into practice. This created a culture in which purpose, accountability, respect, caring, and dialogue was the glue that kept them safe and performing to their individual and team best. They are what books are written about. That evening, I reflected again on the special opportunity I had to join in on these insightful and inspiring discussions. It became clear that what I teach and facilitate is what this group had intuitively and experientially put into practice. Their culture is infused with intrinsic motivation. They are motivated from the inside out. No one is dangling carrots or rewards or threatening them with consequences if they don’t act responsibly. They act safely and responsibly because it matters to them, and they take ownership and pride in it. Self-Determination Theory informs us that if people are given or find a sense of purpose in what they do; if they are given the resources, permission and support to have autonomy in making decisions; the encouragement and opportunity to develop relationships with each other and their managers; and the ability to influence the things that matter most to them—they will not only achieve, they will thrive. This team thrives in a very difficult environment. They do hard and dangerous work. Their success can be framed in a theoretical model, but what is most impressive is their commitment to make it stick—they are the glue. © Tom Wojick, The Renewal Group, September 2012 _ This Mom-ism was almost as regular as her apple pies. I loved my Mom’s apple pies; all that cinnamon and crust made with lard! And I have another memory of her: when she would admonish my sister and me the moment we would start talking unkindly about a neighbor or schoolmate. “If you can’t say something nice, then don’t say anything at all!” That would always shut us up fast. It’s too bad she couldn’t have been on my last business trip – maybe she could have put stop to all the trashing and bashing that was taking place.
I began to notice it while working out in the hotel gym. A woman next to me was high-stepping on an elliptical machine and at the same time trashing and bashing her colleagues to someone on her cell phone. At first I was annoyed at the incessant talking – then I began to notice the tone and content. “She’s nothing but trouble. I’m so tired of her expressing her opinions.” After 30 minutes of this continuous trashing I wanted to start singing “Jingle Bells” as loudly as I could in hopes that she would get the point and quit her conversation. After 40 minutes, I simply gave up and left. Had my Mom been there, she would have put her hand up, motioned to the women to stop, and reminded her, “If you can’t say something nice, then don’t say anything at all.” The next morning while waiting for my 6 am flight I was sitting a few seats away from two copy machine salesmen who were trashing and bashing a customer for wanting too much information and not being able to make up his mind. I could not wait to get on the plane and escape this early morning negative stuff. I’m addicted to caffeine in the morning, but these guys seemed to need a good dose of negativity to get them going. At that point I thought I had escaped the negative white noise. After being upgraded to first class I had visions of reading for a few moments and then retreating into my introverted space until I arrived at my next stop. That bubble burst when two gentlemen behind me felt the need to discuss their perfections and the imperfections and inferiority of their boss and company. I couldn’t help but wonder where my Mom was then. I won’t continue this saga, but I will let you know that it followed me all the way home, which caused me to reflect. Am I this negative and just don’t notice it? Do I live by Mom’s words? Why do we dwell and focus on negativity, weaknesses and mistakes? Are we even conscious of this focus or has it simply become human nature? And there was one more question that really bothered me: have we lost all boundaries of what should be public and private discourse as well as a sense of place and time for these discussions? Has reality TV, YouTube and social networking so blurred the lines of what is personal and professional and private and public that we now accept and treat public space as a stage on which to share how much better we are than all those other people with whom we live and work? It occurred to me that American businesses must be suffering through a crisis of incompetence. If all the people being bashed are as inept as their antagonists claimed, our economy is surely in for another shock. I sensed that the people who were trashing and bashing got a boost of self-esteem from it yet were oblivious to the implications their behavior made about their own character and trustworthiness. Maybe the need to belong is so overwhelming these days that most of us would rather make disparaging remarks about others than take a stand and be heroic and positive. Frankly, we see this in bullying. In most bullying situations you have a “bully,” a victim, and the bully’s cohorts who stand by allowing the trashing and bashing but not actively participating, giving the perception of passive support. The fear of being ostracized has seemingly replaced our primal fear of Saber Tooth Tigers out looking to make a snack of us. A common theme that ran through all of the conversations was self-interest and self-promotion. Had the salesmen taken the time to understand why their client was reluctant to buy their product, they might have had a more fruitful and hopeful meeting. If the woman on the elliptical trainer could step out of her fear of not belonging and frame the other woman’s behavior as being concerned, curious and wanting clarity, she might have an appreciation for her rather than an annoyance with her. And if the two perfect beings unable to find one positive trait in their boss and organization could reflect on the fact that both were selected and still employed by these inferior beings, they might, just might, find a way to be thankful and contribute to finding solutions to their complaints. One reason for these actions, based on human behavior and biology, jumps out at me: stress. There’s little doubt that the past decade has been stressful and the current economic and political climate continues to foment increasing high levels of stress and create we vs. they worldviews. By allowing ourselves to be overwhelmed with this stress, our natural focus is on survival. We may even picture ourselves on a metaphorical Survivor Island, so we plot, connive, lie, and trash and bash our way to being the survivor. What we lose in the process is exactly what we want and need: respect, belongingness, self-worth, and a network of friends and colleagues willing to stand by us and offer assistance. The answer to putting a stop to and reversing this destructive behavior could be as simple as my Mom says: “If you can’t say something nice, then don’t say anything at all.” I don’t mean to make light of this, because it does concern me and it should concern you for no other reason than the realization that the probability that someone is at this moment trashing and bashing you and your organization is greater than you think. Trashing and bashing behavior is a cancer for teams and organizational performance and although our reptile brain says, “Attach or be eaten,” our chances for survival are actually increased by our ability and willingness to care for one other. There are tools and concepts to help individuals and organizations learn how to stop and reverse this negative approach that is taking over and begin to reap the benefits of caring, focusing on strengths and transforming perceived weaknesses and problems into solutions:
To break the habit of trashing and bashing is hard work. The easy path is to find fault and focus on weaknesses instead of courageously finding the strengths in people and the opportunity and potential in difficult situations. It’s easy to jump on the negative bandwagon. But be careful – from what I see, it is already full. Take a different path and resist veering off into the negative – take a few moments and ask yourself, “Is this what I want and how I want to be seen and remembered?” Could you rest in peace with an epitaph that read, “Always ready with a disparaging word and never missed an opportunity to trash and bash even his best friends”? None of us want to be seen or remembered for this destructive and bullying behavior. And it’s time for us to make a commitment to not participate in it actively of passively in either our personal or professional lives. There are many options that we can employ and they all begin with a decision to take a stand. In the end, you will appreciate yourself more for it and find that you have less stress and that people will enjoy and benefit from having a relationship with you. |
Follow us
|



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
